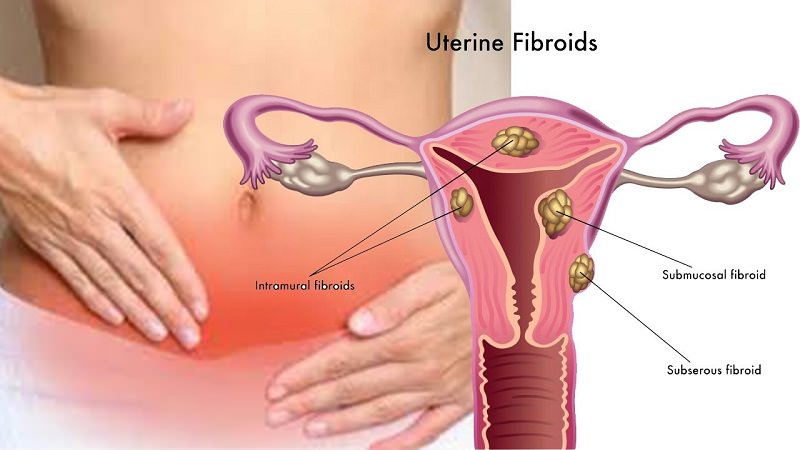
Some women deal with serious health conditions, some of which many find difficult to discuss. One of them is fibroids. These are tumors that develop on the wall of the uterus, but most of them are non-cancerous. A woman suffering from fibroids can have one or multiple fibroids, ranging from the size of an apple seed to grapefruit or melon. Although most are not cancerous, they are a significant public health concern since women play a key role in maintaining family health. If you live with fibroids or suspect you have them, this guide could answer some of your questions about them.
What causes fibroids?
Uterine fibroids could affect any woman, and they are more common as women age. About 60% of women experience fibroids by the age of forties to early fifties. However, many women have also been diagnosed with fibroids when younger, with around 25% of women developing them at 21-30.
There is a link between fibroids and obesity. Obese women and women who consume large amounts of red meat are likely to develop fibroids. According to science, fibroids are controlled by estrogen and progesterone hormones, and having a family member with fibroids increases your risk.
What are the common symptoms of fibroids?
Many women with fibroids do not see any symptoms, but some have difficulty living with them emotionally and physically. Common symptoms of fibroids include:
- Heavy vaginal bleeding which can lead to anemia.
- Pelvic pain or discomfort. It can be mild to severe, and your doctor may recommend pain killers for pelvic pain relief.
- Pressure on the ladder which leads to frequent urination.
- Rectal pressure which leads to lower back pain and constipation.
- Bloating which may result from a large fibroid pressuring the stomach area.
- Discomfort during intercourse which may occur in certain positions or at certain times of the menstrual cycle.
- Emotional distress such as stress, anxiety, depression, distorted body image, and reduced quality of life.
How much bleeding is risky?
Heavy menstrual bleeding results from the distortion of the endometrial cavity caused by the fibroid. A woman with fibroids may experience:
- Periods that last longer than seven days.
- Bleeding between periods.
- Experiencing more than one menstrual period in a month.
- Passing heavy blood clots larger than the size of a golf ball.
- Soaking numerous menstrual products like pads and tampons in only a short time.
You should see a gynecologist or doctor if you have such symptoms.
How does a doctor diagnose fibroids?
A doctor can feel large fibroids during a regular pelvic examination. But they may recommend an ultrasound to identify the location and size of the fibroid. Other imaging technologies such as MRI and X-rays can view the inside of the uterus and fallopian tubes to diagnose fibroids.
What is the treatment of fibroids?
Most women don’t experience any symptoms with fibroids, so they may not require any treatment. But for those with symptoms, the treatment, whether medication or surgery, depends on the individual’s unique needs. Every woman’s uterus is unique, so the treatment the doctor chooses is geared towards relieving one’s specific symptoms. Generally, medical, surgery and radiological treatment depend on the location and size of the fibroid and the woman’s reproductive health goals.